Climate and Climatic zones of Himachal Pradesh
Climate is the statistics of weather over long periods of time. It is measured by assessing the patterns of variation in temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, precipitation, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological variables in a given region over long periods of time. Climate differs from weather, in that weather only describes the short-term conditions of these variables in a given region.
Himachal Pradesh is a northern State and situated the southern of the mighty Himalayas. The State is bordered by Jammu & Kashmir on North, Punjab on West and South-West, Haryana on South, Uttar Pradesh on South-East and China on the East. Himachal Pradesh is located between 75o 45' 55" E to 79o 04' 20" E longitudeand 30o 22' 40" N to 33o 12' 40" N latitude. The height from the mean sea level varies from 350 to 6975 meters. The Climate of any place is dependent on various geographical factors. The state of Himachal Pradesh, India is a hilly region and it experiences a pleasant Climate through out the year. It even experiences heavy snow fall during the winter months. The weather of Himachal alters with the change of altitude.
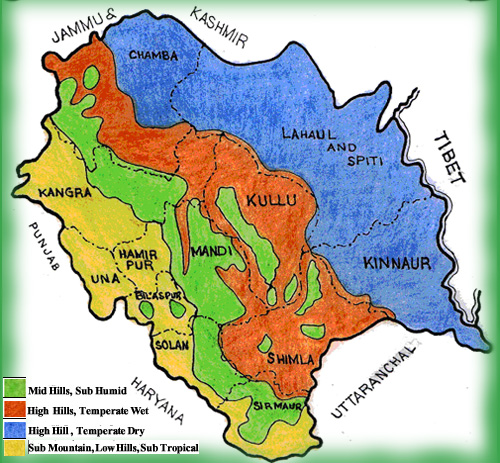
There is great variation in the climatic conditions of Himachal due to extreme variation in elevation. The climate varies from hot and sub-humid tropical in the southern tracts to cold, alpine and glacial in the northern and eastern mountain ranges with higher elevation. The state has areas like Dharamsala that receive very heavy rainfall, as well as those like Lahaul and Spiti that are cold and almost rainless. Broadly Himachal experience three seasons; hot weather season, cold weather season and rainy season. Summer lasts from mid April till the end of June and most parts become very hot (except in alpine zone which experience mild summer) with the average temperature ranging from 28 °C (82 °F) to 32 °C(90 °F). Winter lasts from late November till mid March. Snowfall is common in alpine tracts (generally above 2,200 metres i.e. in the Higher and Trans-Himalayan region).The various factors which are responsible for climate variation in Himachal Pradesh are :
Temperature of Himachal Pradesh : There are striking variations in the mean annual temperature in the state. Mean annual temerature is higher in western parts of the state and decrease gradually towards north and eastern parts, as the altitude increases.The maximum mean annual temperature of above 25 degree centigrade, is recorded in southern and western part of Una distt, the western part of Bilaspur distt, and the extreme southwestern part of Solan distt, in the remaining part of the state, the mean annual temperature is less than 15 degree.
Temperature in general decreases from south to north. The average monthly temperature of the summer months varies from 26 degree celsius in lower outer valleys to 14 degree centgrade in the inner valley zone and that of winter months from 13 degree centgrade to 4 degree centigrade.Temperature also increases with increasing altitude.
Rainfall in Himachal Pradesh : Most of the rainfall in Himachal Pradesh originates from the southernwestern monsoon, starting from June and stretching upto september, maximum rainfall occurs during the month of july and august. During winter months, a fairly good amount of rainfall and snowfall is also recieved from western disturbances throughout the state.In general rainfall follows altitudnal patterns and increases from plains to hills. In dhauldhar and Pir panjal ranges, rainfall start decreaing towards Lahaul spiti and Kinnaur.
Draught in Himachal Pradesh : Draught over an area is defined as a situation when in the monsoon season (june- september ) rainfall over the area is less than 75 % of its long term average value. Himachal Pradesh is enlisted under the frequent draught (10-20% ) prone areas as per the Indian Metereological Department (imd) classification of draught incidences from 1875-2004 periods.
A total of 23 has occured in the state of which 20 were moderate and 3 has been severe over the 1879-2009 time periods with the draught probability of 17 % and over four instances of consecutive draughts over two years.
According to geographical features of Himachal Pradesh , it has 3 climatic zones of Himachal Pradesh :
1. SHIVALIK HILL ZONE : Climate Sub Tropical, consists of foothills and valley area from 350 to 650 meters above mean sea level, It occupies about 35% of the geographical area and about 40% of the cultivated area of the State. The major crops grown in this Zone are Wheat, Maize, Paddy, Gram, Sugarcane, Mustard, Potato, Vegetables etc.
2. MID HILL ZONE: This zone extends from 651 meters to 1,800 meters above mean sea level. Having mild temperate climate. It occupies about 32% of the total geographical area and about 37% of the cultivated area of the State, The major crops are Wheat, Maize, Barley, Black Gram, Beans, Paddy etc. This zone has very good potential for the cultivation of cash crops like Off-Season Vegetables, Ginger and production of quality seeds of temperate vegetables like Cauliflower and root crops.
3. HIGH HILL ZONE : It lies from 1,801 to 2,200 meters above sea level with humid temperate climate and alpine pastures. This zone covers about 35% of the geographical areas and about 21% of the cultivated area of the State. The commonly grown crops are Wheat, Barley, Lesser Millets, Pseudo-cereals (Buckwheat and Amaranthus), Maize and Potato etc. The area is ideally suited for the production of quality seed Potato and temperate Vegetables. This zone possesses good pastures and meadows.
4. COLD DRY ZONE : It Comprises of Lahaul-Spiti and Kinnaur Districts and Pangi Tehsil of Chamba District lying about 2,200 meters above mean sea level. It occupies about 8% of the geographical and 2% of the total cultivated area of the State. The major crops grown are Wheat,Barley, Pseudo-cereals like Buck wheat and Amaranthus. It is ideally suited for the production of quality Seed Potato, temperate and European type of Vegetables and their Seeds, Seed Potato, Peas as green and seed purposes.
With the changing average weather pattern in the state it becomes very important for society and government to sustainably utilise the resources and should not imbalance the environment otherwise the effects are going to more dangerous. Many places have seen changes in rainfall, resulting in more floods, droughts, or intense rain, as well as more frequent and severe heat waves. The planet’s oceans and glaciers have also experienced some big changes – oceans are warming and becoming more acidic, ice caps are melting, and sea levels are rising. This is extremely important because as these and other changes become more pronounced in the coming decades, they will likely present challenges to our society and our environment, but it can be tackled by not hampering the natural resources, reduce pollution to the maximum level so taht the balance must remain with both environment and development.