Soil and Water Conservation Programmes of Agriculture Department in Himachal Pradesh
Soil and Water conservation is an integral component of Agriculture production in particular and environment protection programme in general. Himachal Pradesh is a hilly terrain with rolling topography and sloppy lands.The rain fall is high in rainy season which add the problems of soil and water conservation, where water scarcity is experienced in other seasons. Keeping in view, the importance of soil and water conservation, the Department of Agriculture is implementing rain water harvesting, soil conservation and soil erosion control schemes including Individual, Community based tank and Head weirs etc. under various schemes run by the Department to increase the agriculture production.
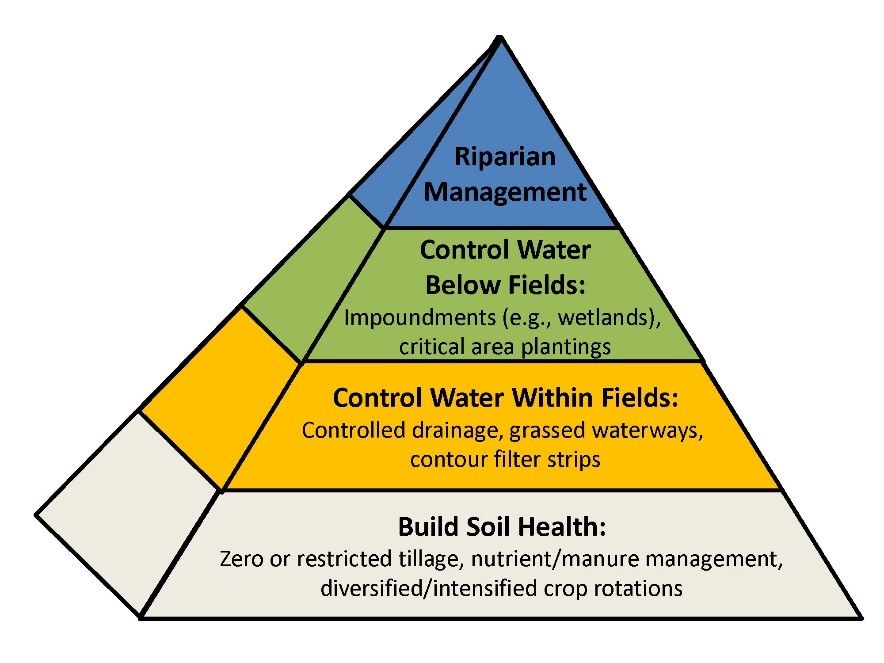
The detail of various measures adopted for soil and water conservation programme are as under:
A) Biological Measures :
Biological or vegetative measures are preferred in watershed development programmes as they are eco- friendly, sustainable and cost effective. These measures are normally adopted on lands milder slopes, less runoff and sediment flow.
Objectives
- To reduce splash erosion by moderating the impact of rain drops.
- To reduce runoff velocity and increase infiltration opportunity time
- To slow down wind speed .
- To trap fine soil and nutrients, and
- To improve physio-chemical properties of the soil and help in conserving moisture in low rainfall areas.
Types of Biological Measures:-
- Vegetative Barriers.
- Alley Cropping
- Ley Cropping
- Strip Cropping,
- Contour Farming
- Land Configurations.
- Tillage
- Mulching
- Residue Management.
B) Mechanical Measures:-
Where biological measures only are insufficient to check erosion to a desired level due to high velocity of run off or discharge , mechanical measures are needed. The mechanical measures not only check soil erosion but also conserve moisture for crop growth. Basically these measures constitute a series of mechanical barriers constructed across the slope to reduce or break the length of slope only or both the length and degree of slope to dissipate the energy of flowing water.The selection and suitability of engineering control measures to be adopted under different locations depend on soil depth, rainfall, land slope and crops to be raised.
•Bunding
•Terracing
•Leveling .
•Diversion drains.
•Contour Trenches.
•Stone Walls.
•Retaining Walls.
C) Drainage Line Treatment:-
Drainage line which carry runoff and sediment flow. They may have different forms such as drainage channels, gullies, natural / artificial waterways, streams, rivers or torrents.
Objectives:-
•Check soil erosion in the channel bed and adjoining lands.
•Improve moisture for biomass production.
•Protect banks/side slopes from undercutting or scouring.
•Recharge ground water.
•Flow guidance, bank protection and / or land reclamation in the downstream torrents.
Depending upon their location and objectives, the measures for drainage line treatment may be mainly grouped as :?Gully /Channel stabilization measures.
- Check Dams.
- Live Check Dams/ Vegetative Barriers. Temporary check dams.
- Permanent structures for gully stabilization /water harvesting.
- Drop Spillway
- Drop inlet spillway
- Torrent and stream bank erosion control measures.
- Spurs.
- Vegetative Retards.
- Protection / Toe walls
- Revetments.
D) Rainwater Harvesting Techniques:-
A. In situ Rainwater Harvesting :
1. Bunding and terracing
2. Vegetaive contour barriers.
3. Land leveling
4. Contour ditching.
5. Grades border strips
6. Contour farming.
7. Cover crops and mulching
8. Conservation tillage and deep ploughing
9. Contour trenching
B. Rainwater /Direct Surface Runoff Harvesting :
1. Rooftop Collection /rainwater cistern.
2. Dugout pond /storage tanks.
3. Diversion Bunds/ channel
4. Water spreading
C. Stream Flow or Runoff Harvesting:
1. Gully control structures/ check dams
2. Water harvesting dams / stop dams
3. Water diversions
4. Ponds
These schemes are taken up on the demand of local farming community/ public representatives and are based on feasibility reports counting various technical factors. These sanctioned schemes are then executed purely in participatory mode and as per RIDF ( Rural Infrastructure Development Fund ) guidelines( Guidelines stand approved by the Govt.) i.e. through Water Users Associations (WUA) by involving the beneficiaries of schemes.
Water users associations elect a Krishak Vikas Sangh (KVS) for each scheme and the same is registered under Societies Registration Act 2006. KVS execute these schemes under technical guidance of the Department. The operation and maintenance of the executed schemes is entrusted to the KrishakVikasSangh after its completion.
1) Rashtriya Krishi VikasYojna (RKVY )
i) TheDepartment of Agriculture is executing Community Based Water Harvesting & Flow irrigation Scheme on community basis.
ii ) The department is providing financial assistance for c/o water harvesting structures , farm ponds and tanks on community based schemes. 100% expenditure is borne by the Govt. of India with an objective to achieve 4% growth in agriculture sector.
Basic Objectives of Scheme:
1. Recharging of ground water.
2. Reduction in soil loss.
3. Production of Fish Culture.
4. Reduction in flush floods.
5. Mitigation of draught.
6. Better environment conditions in the catchment.
7. Reduction in drainage density.
8. Higher availability of water for drinking and other domestic needs.
9. Higher availability of other needs like fuel and fodder.
During the year 2007-08, The Department has executed 98 Minor irrigation Schemes / Water Harvesting Structures with an expenditure of Rs. 324.54 lakh . 29 projects of Minor Irrigation were executed with an expenditure of Rs. 350.61 lakh during the year 2008-09 and a provision of Rs. 327.24 is required to complete these 29 schemes during 2009-10 .
2) Integrated Watershed Management, theDepartment of Agriculture is constructingCommunity Based Water Harvesting Structures, Silt retention structure in R.C.C. , Concrete, masonry and Check dams in wire crate mesh etc on 100% assistance to provide protective / life saving and assured irrigation.During the financial year, 2008-09, Rs 100 lakh have been provided under this scheme. The schemes are executed through participatory approach and cover engineering and vegetative measures. This is a State Plan
Scheme.
3) Macro Management of Agriculture Central / State assistance (90%&10 % )
- Under this scheme, assistance is available to individual farmers for construction of, shallow wells and Bore wells. The assistance @ 25% limited to Rs 12500/- to small and marginal farmers .
- Assistance ranging from Rs8000/- to Rs 1.00lac with minimum land holding of 0.08 ha and maximum of 2hactare. is also available to small and marginal farmers for the installation of Water Lifting devices.
- 100% financial assistance is also available under community based water harvesting schemes/ tanks/ ponds / water conveyance system and land protection schemes with a ceiling of Rs 50000/- per hectare. Budget outlay 50lac.
- National Water shed Development Programme for Rain fed Areas under Centrally assisted Macro Management of Agriculture Scheme, duringXIth Plan ,40 new watersheds have been selected in 9 districts (
- except Una and Tribal ) with an estimated cost of Rs 1490.21 lakh to treat an area of 24,836 hectares. Out of Rs 1490.21 lakh , 50% of funds shall be spent on Natural Resource Management component. During theyear,2007-08 , Rs 144.26 lakh have been spent on various activities and for the year 2008-09 , a provision of Rs 152 lakh is made to treat an area of 4500 hectares under Soil and Water Conservation. The above stated activities like Biological measures , mechanical measures , drainage line treatment and water harvesting are executed under this programmed.
4) On Farm Water Management( SCA) ( Special Committee on Agriculture ) Individual Tanks, assistance is provided to schedule cast Farmers for the construction of individual Tank of minimum size of 9 cum @ 33% limited to Rs 8000/-. During the financial year, 2009-10, Rs 46 lakh have been provided under this scheme.
5) RIDF programme of NABARD : The Department of Agriculture is constructing Minor Irrigation Schemes such as Lift Irrigation, Flow Irrigation , Shallow & Deep Tube well schemes and Community Based Water Harvesting Schemes on 100% assistance to provide protective / life saving and assured irrigation.
- During the year 2007-08, 109 Minor irrigation Schemes / Water Harvesting Structures were executed with an expenditure of Rs. 958.27 lakh .
- During the year 2008-09 , 13 projects of Water Harvesting and Natural Resource Management and 19 Projects of Minor Irrigation were executed with an expenditure of Rs.1198.08 lakh and 32 Minor Irrigation Schemes / Shallow Tube wells/ Water Harvesting projects amounting to Rs. 846.36 lakh have been posed to NABARD for funding under RIDF- XV after attending the observations and sanction is awaited.
- The budget allocation of Rs 219.20 lakh has been made for the execution of 4 schemes of Water Harvesting and Natural Resource Management sanctioned under RIDF- XIV during the year 2009-10.
- Besides this, the Department of Agriculture has prepared two projects i.e Production of Cash Crops through adoption of Precision Farming practices through Poly house cultivation -Part-I and Project on Diversification of Agriculture through Micro-Irrigation and other related Infra-Structure in Himachal Pradesh-Part-II under Pt Deen Dayal Kisan BagwanSamridhi Yojna. The projects would be implemented in all the Distts. of the state with an outlay of Rs. 353.01 Crores. Major emphasis has been laid on the creation of need based infrastructure for the production of cash crops. For the creation of need based infrastructure, special and enhanced assistance would be provided to the eligible and deservering farming community. The projects would be completed during the 11th five year plan as per approval given by the funding agency i.e. NABARD under RIDF-XIV.
Conclusion :
Agriculture in Himachal Pradesh is a way of life for the agrarian population and nearly 70% population is directly or indirectly dependent on this sector. Presently, farming and farmers of Himachal Pradesh are passing through a transitional phase, state govt. has allocated 12 % of its plan resources for agriculture and allied sectors, which is highest in the country and also now state is promoting organic farming in a big way. Efforts are afoot to make Himachal Pradesh self sufficient in agriculture production and also improving the economy of the state.